Structural Engineering Research
-
Utilizing I-shaped link as a shear damper for improving the behavior of CBF braces, an numerical and parametrical study
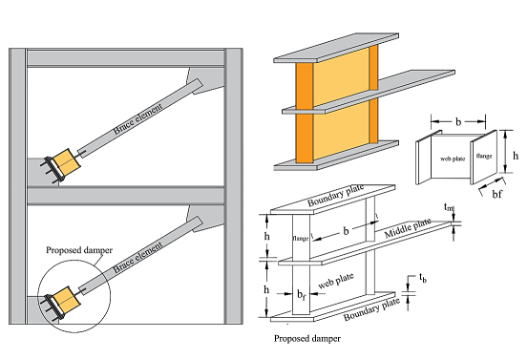
Researcher:
Byungik Chang, Professor of Civil Engineering and Nadia M. Mirzai, Post-Doctoral FellowProject Description:
Although Concentrically Braced Frame (CBF) is a system with high lateral stiffness, buckling under compressive forces has made it a system with weakness in ductility and not appropriate enough for high seismic zones. In this study, a new metallic damper, which can be simply constructed, employed in CBF, and replaced after severe earthquakes, is investigated. This damper includes two shear panels that act as an I-shaped shear link beam for the energy dissipation aim.Status:
CompletedDissemination:
Journal of Constructional Steel Research
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2022.107482 -
Structural Analysis of Abutment Concrete Cut-out for Safety Niche
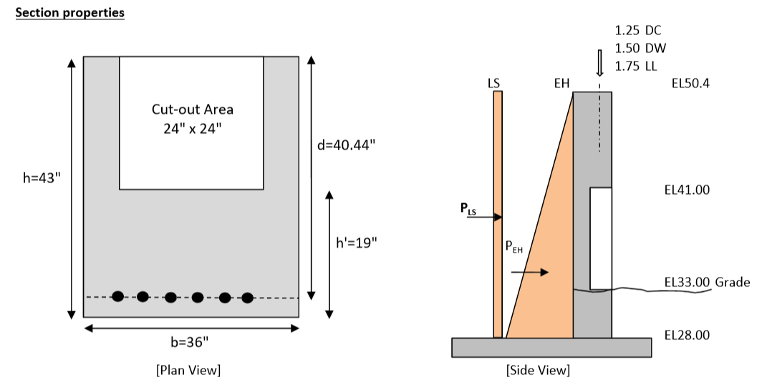
Advisor:
Byungik Chang, Professor of Civil EngineeringGraduate Student:
Thippesh Bethur HanumanthareddySponsor:
Provost AssistantshipProject Description:
An abutment is one of the main components in the bridge. Safety niche is a cut-out on a portion of abutment which act as a temporary shelter for bridge working. A finite element analysis for the investigation of effect of positioning Safety niche along the reinforced concrete Abutment in a bridge will carry and result will be recordable. Any change in abutment may cause damages to the concrete abutment and encounter the bridge structure in danger. Flexural behavior of concrete is an important factor in view of creating a growing crack in cut-out in abutment. -
Development of a Nomogram to Predict the Maximum Contact Stress Between a bridge I-Girder and a Support Roller
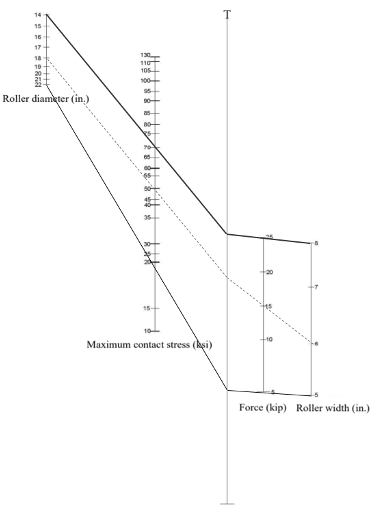
Advisor:
Byungik Chang, Professor of Civil EngineeringGraduate Student:
Thanin ChanmalaiSponsor:
Provost AssistantshipProject Description:
An abutment is one of the main components in the bridge. Safety niche is a cut-out on a portion of abutment which act as a temporary shelter for bridge working. A finite element analysis for the investigation of effect of positioning Safety niche along the reinforced concrete Abutment in a bridge will carry and result will be recordable. Any change in abutment may cause damages to the concrete abutment and encounter the bridge structure in danger. Flexural behavior of concrete is an important factor in view of creating a growing crack in cut-out in abutment.Status:
CompletedDissemination:
https://doi.org/10.5267/j.esm.2021.7.001 -
Moment Distribution Factor of Floor Beams for a Two-girder Bridge
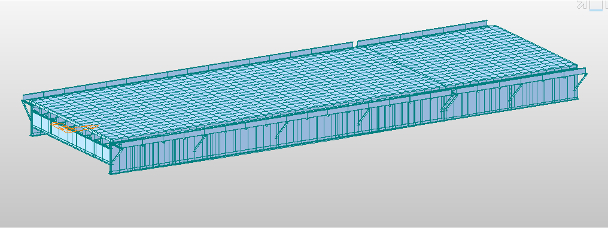
Advisor:
Byungik Chang, Professor of Civil EngineeringGraduate Student
Saron G. HagosSponsor:
Provost AssistantshipProject Description:
A two-girder bridge consists of concrete deck, stringer and floor beams. There is no guideline in determining live load moment distribution factor for floor beams. A computer-aided structural analysis will be conducted to obtain the live load moment distribution of the floor beams for a two-girder bridge.Status:
Progress -
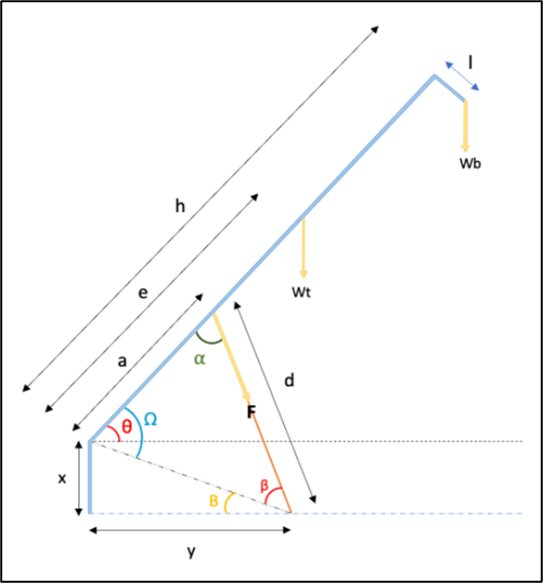
Analysis of Optimum Position for Hydraulic Cylinders Utilized in Wind Tower Erection
Advisor:
Byungik Chang, Professor of Civil EngineeringGraduate Student
Anbesh Rawal and Kevin MisaroSponsor:
Graduate Engineering Endowed Fellowship
Provost Assistantship
CT NASA Space GrantProject Description:
Introduction of alternative technologies relating to the tilt-up method of wind turbine erection have reinvigorated the proposed energy objectives. By way of hydraulic cylinders, which are incorporated as a component of the wind towers, and the introduction of a hinge joint slightly above the base of the tower, turbines can be put up and laid down with ease. Despite this revolutionary discovery, the load bearing capacity of these cylinders, as well optimal position selection, are imperative to avoid any unexpected accidents. This discovery can prove priceless in achieving the preset goals for energy.Status:
Ongoing -
Structural Analysis of Historical Structures
Advisor:
Goli Nossoni, Associate Professor of Civil Engineering and Byungik Chang, Professor of Civil EngineeringGraduate Student
Harshitha PeddakantiSponsor:
Graduate Engineering Endowed FellowshipProject Description:
The proposed study will feature a comprehensive evaluation of the Perry Memorial Arch. This entails utilizing scaled models of the Perry Memorial Arch to determine general dimensions. Additionally, a conclusive material evaluation will be conducted so as to know all constituent entities that make up the structure.Status:
Progress -
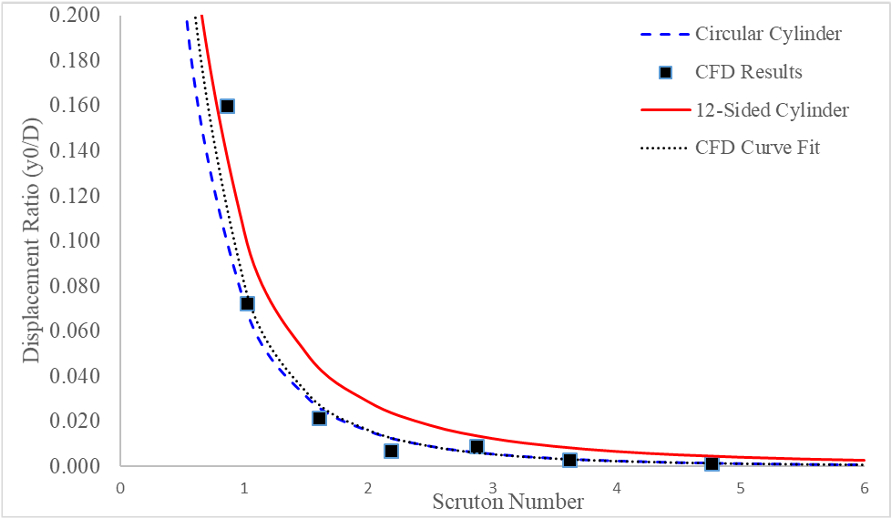
Development of Aerodynamic Parameters for a Multi-sided cylinder using Computational Fluid Dynamics
Advisor:
Byungik Chang, Professor of Civil EngineeringGraduate Student
Christopher OngSponsor:
Provost AssistantshipProject Description:
High mast light poles (HMLP) are used nationwide on major interstates and at local intersections for luminary purposes in the United States. The HMLPs are subjected to major oscillatory wind loading which may cause fatigue and earlier life expediency failure. Numerical modeling with the use of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is proposed to simulate the typical shape (dodecagonal cylinders) of the HMLPs and be validated with wind tunnel experiments.Status:
CompletedDissemination:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2020.104130 -
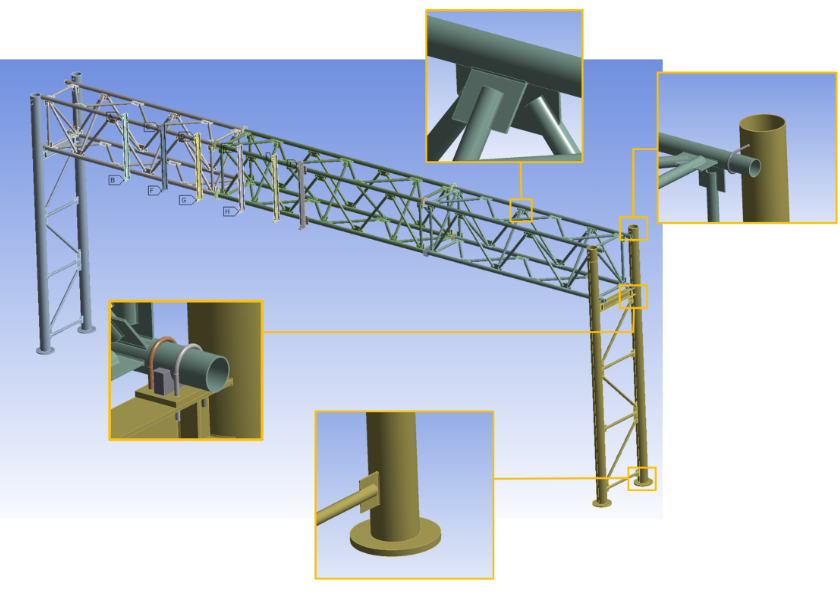
Thermal Induced Fatigue of Overhead Truss Structures
Advisor:
Byungik Chang, Professor of Civil EngineeringGraduate Student
Christopher OngUndergraduate Student
Jongsung LeeSponsor:
Iowa DOT and Iowa State UniversityProject Description:
Dynamic Messaging Signs (DMS) are found in operation over freeways, expressways, and other major intersection that provide information to travelers. If the DMS structure fails, then pedestrians and motorists can be harmed. The objective of this study is to analyze thermal induced fatigue life of highway overhead support structures. Field monitoring, mathematical analysis and finite element modeling were employed to perform the objective. The finite element modeling extends to two different type of connection (Slotted gusset welded joints and tube-to-tube welded joints) and two different materials (structural steel and aluminum alloy). Based on the estimated fatigue life for the overhead truss structures, structural steel slotted gusset welded connection type provides larger fatigue life than other cases.Status:
CompletedDissemination:
https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CF.1943-5509.0001416 -
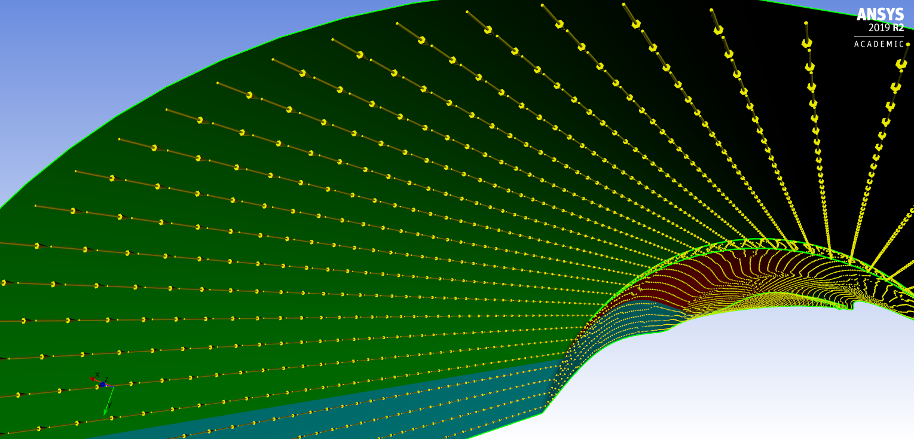
Structural Evaluation of a Multi-bladed Horizontal Wind Turbine Using Numerical Modeling
Advisor:
Byungik Chang, Professor of Civil EngineeringGraduate Student
Omar Morales EscuderoSponsor:
StarWind, VTProject Description:
A comparative analysis was done between the baseline and two proposed blades, taking into consideration the structural resistance and the safety factors recommended by certification agencies. Several benefits were found in the use of balsa wood as a core material, improving the buckling capacity, based on DNV GL guidelines, and keeping the weight low when compared with the original design. On the other hand, the addition of a third shear web for the other solution demonstrated a practical approach to increase the stiffness behavior and guarantee a safe area of buckling under IEC guidelines.Status:
CompletedDissemination:
Confidential -
Serviceability analysis and feasibility study of rooftop PV system on commercial building in New York City.
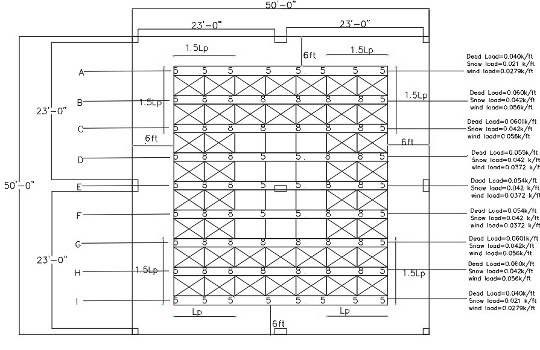
Advisor:
Byungik Chang, Professor of Civil EngineeringGraduate Student
Daniel Adamu ShedoSponsor:
TCoE Graduate Research FellowshipProject Description:
The project is mainly focused on uplift wind calculation to determine the optimal number of required ballast, roof slab serviceability analysis to determine sustainability in the form of long-term deflection, and a feasibility study on economic benefits of PV installation. A continuous two way reinforced concrete slab which can be a representative case for New York City’s buildings’ roof top has been selected and analyzed. It is assumed that the building has undergone regular maintenance that will avoid substantial deflection at the start of the analysis and the building is classified under risk category II. Building heights of 80ft, 60ft and 40ft were used. A total of 18 cases based on height and exposure class were modeled using finite element modeling software to analyze Pre and Post PV installation deflections. Economic Feasibility study for PV installation was also conducted.Status:
CompletedDissemination:
Under review